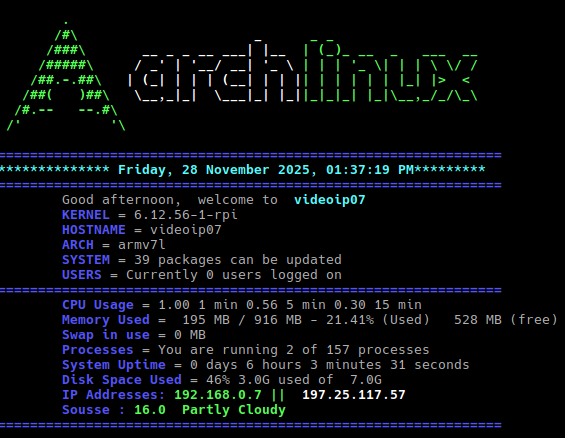
1. What is motd and how it works
The motd file, which stands for "message of the day," , functions as a system-wide file that shows a static or dynamically created message to users at the time of their login but before their shell starts. It's used by administrators to share important information like system updates, maintenance notices, or other relevant news with all users who log in to the system. The message is typically found in the /etc/motd file. On many modern systems, the MOTD is dynamically generated by scripts located in directories like /etc/update-motd.d/. These scripts can run at login to display current system information, such as uptime, disk usage, or network status. The pam_motd module is often responsible for displaying the message of the day after a successful login
2. motd for Arch Linux Systems
For a system based on Arch Linux the easiest way is to use the script from Luis Felipe Sanchez Github repository as a basis and customize it according to our needs.
- Install git
sudo pacman -S git - Clone the repository and launch the script dedicated to arm devices
git clone https://github.com/lfelipe1501/Arch-MOTD.git cd Arch-MOTD sudo sh update_motd-pi.sh - Copy the script
sudo cp update_motd-pi.sh /usr/bin/update_motd.sh && sudo chmod 775 /usr/bin/update_motd.sh - Edit the files in /etc/pam.d
We have to edit system-login and sshd files :
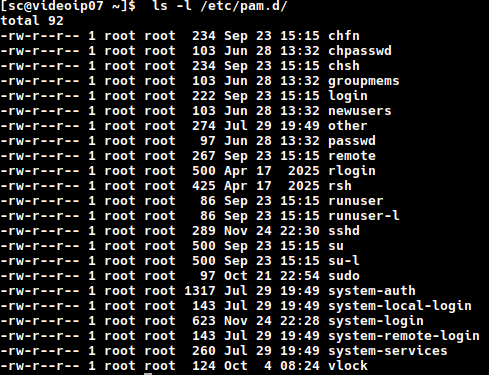
- system-login file
Cut this line for further use in sshd file : session optional pam_motd.so motd=/etc/motd
sudo nano /etc/pam.d/system-login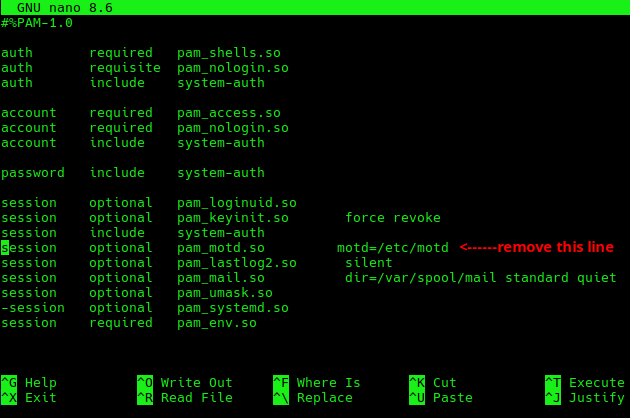
- sshd file
Paste the deleted line at the end of the sshd file and add an a line to make pam.d execute the script update_motd.sh
sudo nano /etc/pam.d/sshdAdd these two lines :
session optional pam_exec.so stdout /usr/bin/update_motd.sh
session optional pam_motd.so motd=/etc/motd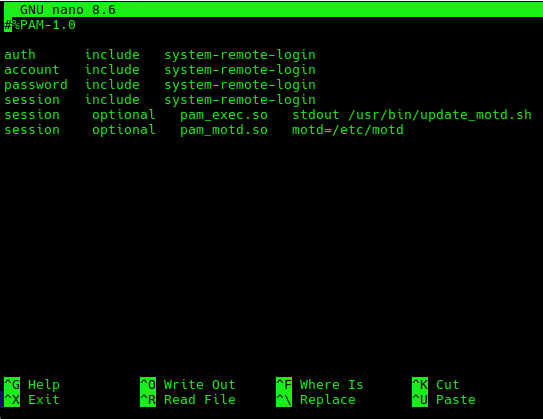
- Logout and login again using ssh should give the basic motd display described here
3. Customize the script update_motd.sh
We can add other useful informations such as percent of memory in use, swap, local and external IP, and weather info.
To get weather info i used the API from weatherapi.
After registering we get an API key which can be used to display weather info. Their free plan is enough for personal use.
3.1 Install jq
jq is a powerful, lightweight, and flexible command-line JSON processor designed for parsing, filtering, and manipulating JSON data. It functions like sed or awk for JSON, allowing for intricate transformations and extractions.
jq takes JSON input, typically piped from another command or read from a file, and outputs transformed JSON to standard output. jq operates through filters, which are expressions that transform an input JSON value into an output JSON value. Filters can be chained together using pipes (|) to create complex operations.
sudo pacman -S jq

 According to weatherapi, it is possible to use GPS coordinates for our location to avoid wrong results (using Sousse as a location displayed results related to another city that likely shares the same name..). Next, we create two variables in update_motd.sh to gather weather info :
According to weatherapi, it is possible to use GPS coordinates for our location to avoid wrong results (using Sousse as a location displayed results related to another city that likely shares the same name..). Next, we create two variables in update_motd.sh to gather weather info :
API_KEY="OUR_API_KEY"
weather_temp=$(curl -s "http://api.weatherapi.com/v1/current.json?key=$API_KEY&q=35.8245,10.6346&aqi=no" | jq -r '.current.temp_c')
weather_desc=$(curl -s "http://api.weatherapi.com/v1/current.json?key=$API_KEY&q=35.8245,10.6346&aqi=no" | jq -r '.current.condition.text')We can also add a translation to french by using substitute command in Sed :
weather_desc_fr=$(echo "$weather_desc" | sed '
s/Patchy rain nearby/Averses à proximité/g;
s/Overcast/Couvert/g;
s/Partly cloudy/Partiellement nuageux/g;
s/Sunny/Ensoleillé/g;
s/Rain/Pluie/g;
s/Clear/Ciel dégagé/g;
')3.2 Install other dependencies
sudo pacman -S inetutilsThe hostname command is part of GNU inetutils package. Finally :